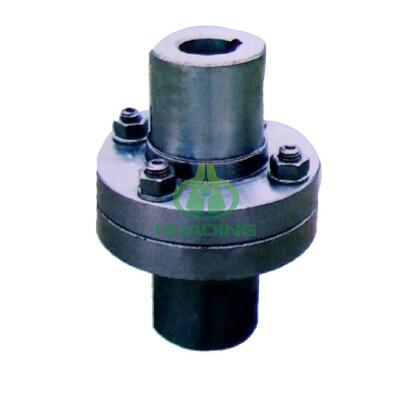
The main difference between rigid and flexible flange couplings lies in their ability to accommodate misalignment and flexibility. Both types of couplings are used to connect two shafts in machinery, but they serve different purposes based on the requirements of the application. Let's explore the key differences between rigid and flexible flange couplings:
1. Flexibility:
Rigid Flange Coupling: As the name suggests, rigid flange couplings offer little to no flexibility. They provide a solid and inflexible connection between the shafts, ensuring precise alignment and efficient torque transmission. Rigid couplings are suitable for applications where shafts need to be in perfect alignment and where flexibility is not necessary.
Flexible Flange Coupling: Flexible flange couplings, on the other hand, are designed to accommodate slight misalignments between the connected shafts. They have some degree of flexibility, which allows them to absorb angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, reducing stress and wear on the shafts and bearings. Flexible couplings are ideal for applications where there may be some level of misalignment or where shock and vibration absorption are necessary.

2. Misalignment Tolerance:
Rigid Flange Coupling: Rigid couplings have minimal misalignment tolerance. They require precise alignment between the shafts during installation to prevent premature wear and vibrations. Any misalignment in a rigid coupling can lead to increased stress on the shafts and may result in mechanical failures over time.
Flexible Flange Coupling: Flexible couplings can handle some degree of misalignment, which makes them more forgiving in real-world applications. They can compensate for minor misalignments, reducing the need for precise shaft alignment during installation.
3. Torque Transmission:
Explore more:What is a Mechanical seal?Exploring the Versatile Uses of Electronic ActuatorsThe Power of Precision: Plane Thrust Ball BearingsHow Do Indexable Tools Keep Their Edge?Parts of a ball valveWhat is the stator in a DC motor?What is cylindrical gears?Rigid Flange Coupling: Rigid couplings efficiently transmit torque from one shaft to another, offering accurate and reliable torque transmission. They are suitable for applications that require precise and synchronized motion.
Flexible Flange Coupling: Flexible couplings also transmit torque effectively, but they can absorb shock loads and vibrations, making them more suitable for applications where shock and vibration dampening are necessary.
4. Applications:
Rigid Flange Coupling: Rigid couplings are commonly used in applications where precise alignment and torque transmission are critical. They are often found in power transmission systems, machine tools, and other applications where shafts must rotate in perfect synchronization.
Flexible Flange Coupling: Flexible couplings are widely used in various industrial applications, especially in machinery where there may be slight misalignments, vibrations, or shock loads. They are common in pumps, compressors, conveyors, and other equipment where flexibility and shock absorption are essential.
In summary, the main difference between rigid and flexible flange couplings is their flexibility and misalignment tolerance. Rigid couplings offer a solid and inflexible connection with precise torque transmission, while flexible couplings provide some degree of flexibility to accommodate misalignments and dampen vibrations. The choice between the two types depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the need for precise alignment, flexibility, and shock absorption.
Explore more:How does a 1-inch diaphragm pump work?What is precision surface finishing?Where can EVI DC Inverter Heat Pumps be used?What is an Off-Highway Vehicle Controller?What is bellow seal globe valve?What are Applications of Gravel Pumps?What are the benefits of Flat Wire Compression Springs?










Comments
Please Join Us to post.
0