Lithium aluminium deuteride, also known as LiAlD4, is a compound that holds significant importance in various scientific and industrial fields. This compound, derived from the combination of lithium, aluminium, and deuterium, possesses unique properties and finds applications in diverse areas of research and technology. In this article, we will explore what lithium aluminium deuteride is, delve into its properties, discuss its synthesis methods, and highlight its wide-ranging applications.
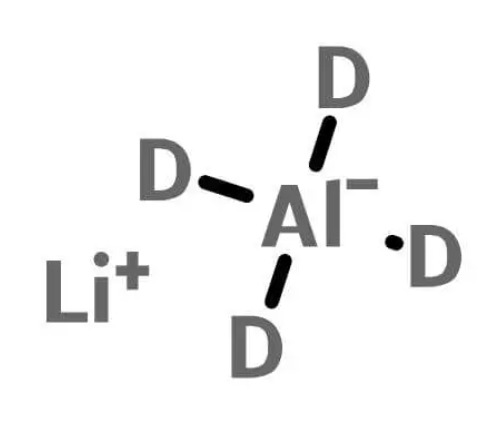
At its core, lithium aluminium deuteride is an inorganic compound composed of lithium (Li), aluminium (Al), and deuterium (D). Deuterium, a stable isotope of hydrogen, replaces the typical hydrogen atoms found in lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4). The substitution of deuterium for hydrogen imparts distinct characteristics to the compound, making it valuable in various chemical and scientific processes.
One of the key properties of lithium aluminium deuteride is its ability to serve as a powerful reducing agent. It exhibits remarkable reactivity towards a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds. This reactivity stems from the high hydrogen content in the compound, with each deuterium atom capable of donating a hydride ion (H-) during chemical reactions. This characteristic makes lithium aluminium deuteride an essential component in many organic synthesis procedures, such as the reduction of carbonyl compounds to alcohols or the conversion of nitro groups to amines.
The synthesis of lithium aluminium deuteride involves the reaction of lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) with deuterium gas (D2). This reaction results in the replacement of hydrogen atoms in lithium aluminium hydride with deuterium. The process typically requires careful handling due to the reactivity of the compounds involved and is conducted under controlled conditions to ensure safety and efficiency.
Once synthesized, lithium aluminium deuteride requires specific storage and handling protocols. It is highly sensitive to air and moisture, and exposure to these elements can lead to decomposition and the release of deuterium gas. Therefore, proper storage in air-tight containers, preferably in an inert atmosphere, is crucial to maintain the compound's stability and purity. Additionally, handling lithium aluminium deuteride requires precautions to prevent contact with moisture, which could result in hazardous reactions.
The applications of lithium aluminium deuteride span a wide range of fields. In the realm of chemistry, it is employed as a reagent for various reduction reactions, enabling the synthesis of complex organic compounds. It finds use in pharmaceutical research, where its reducing properties aid in the development of new drugs and medications. Moreover, lithium aluminium deuteride plays a role in the production of isotopically labeled compounds, essential for studying reaction mechanisms and conducting kinetic studies.
In addition to chemistry, lithium aluminium deuteride finds applications in other scientific disciplines. In the field of nuclear energy, it serves as a neutron moderator, helping to control the rate of nuclear reactions. This property is significant in research reactors and other nuclear facilities. Furthermore, lithium aluminium deuteride is used in neutron detectors, enabling the measurement and monitoring of neutron radiation.
In conclusion, lithium aluminium deuteride is an important compound with diverse applications in chemistry, nuclear energy, and scientific research. Its unique properties as a reducing agent and neutron moderator make it valuable in a wide range of processes and studies. Understanding the nature of lithium aluminium deuteride, its synthesis, and its applications opens doors for advancements in various scientific and industrial fields, paving the way for innovative solutions and discoveries.




Comments
Please Join Us to post.
0